Navigating the world of investments can be tricky, and the cannabis industry, being relatively new and rapidly evolving, presents its own unique set of complexities. When you start digging into it, you might come across the term “thinly traded cannabis stocks.” This refers to shares of cannabis companies that don’t see a lot of buying and selling activity on the stock market. Think of it like a quiet street compared to a bustling city center – fewer cars, fewer pedestrians, and sometimes, less predictable movements.
This article will dive into what thinly traded cannabis stocks are all about, why they might be thinly traded, and what it means for someone like you who might be considering investing in them. We’ll explore both the exciting potential and the significant risks involved, all while keeping it in plain, easy-to-understand English. Our goal is to equip you with the knowledge to approach these investments with eyes wide open, ready for whatever the market might throw at you.
What Exactly Are Thinly Traded Stocks?
First things first, let’s break down “thinly traded.” In simple terms, a thinly traded stock is one where there’s a low volume of shares being bought and sold on a given day. This means there aren’t many active buyers and sellers, which can have a big impact on how the stock behaves. Imagine trying to sell a rare antique – if only a few people are interested, you might have to wait a while or accept a lower price than you hoped. The same principle applies here.
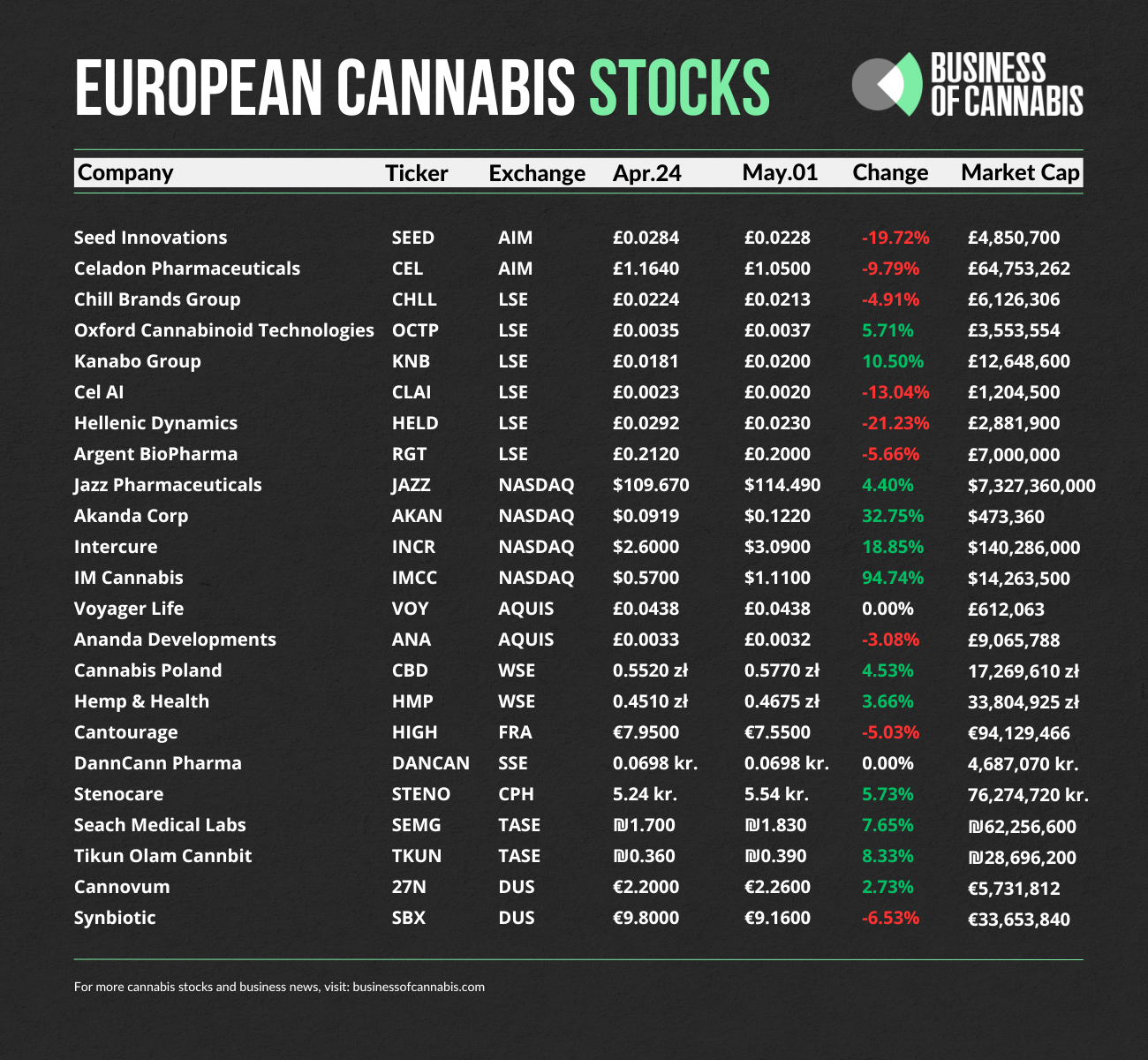
You can often spot thinly traded stocks by looking at their daily trading volume. If a stock consistently trades only a few thousand shares a day, or even a few hundred, it’s likely thinly traded. Another tell-tale sign is a wide “bid-ask spread.” This is the difference between the highest price a buyer is willing to pay (the “bid”) and the lowest price a seller is willing to accept (the “ask”). In highly liquid, or “thickly traded,” stocks, this spread is usually very narrow, perhaps just a few pennies. But with thinly traded stocks, that gap can be much wider, sometimes several cents or even more, making it harder to get a fair price when you want to buy or sell.
Why Are Some Cannabis Stocks Thinly Traded?
The cannabis industry is a fascinating space, but it’s also a relatively young one, particularly when it comes to publicly traded companies. Several factors contribute to why some cannabis stocks end up being thinly traded:
The Wild West of Regulation
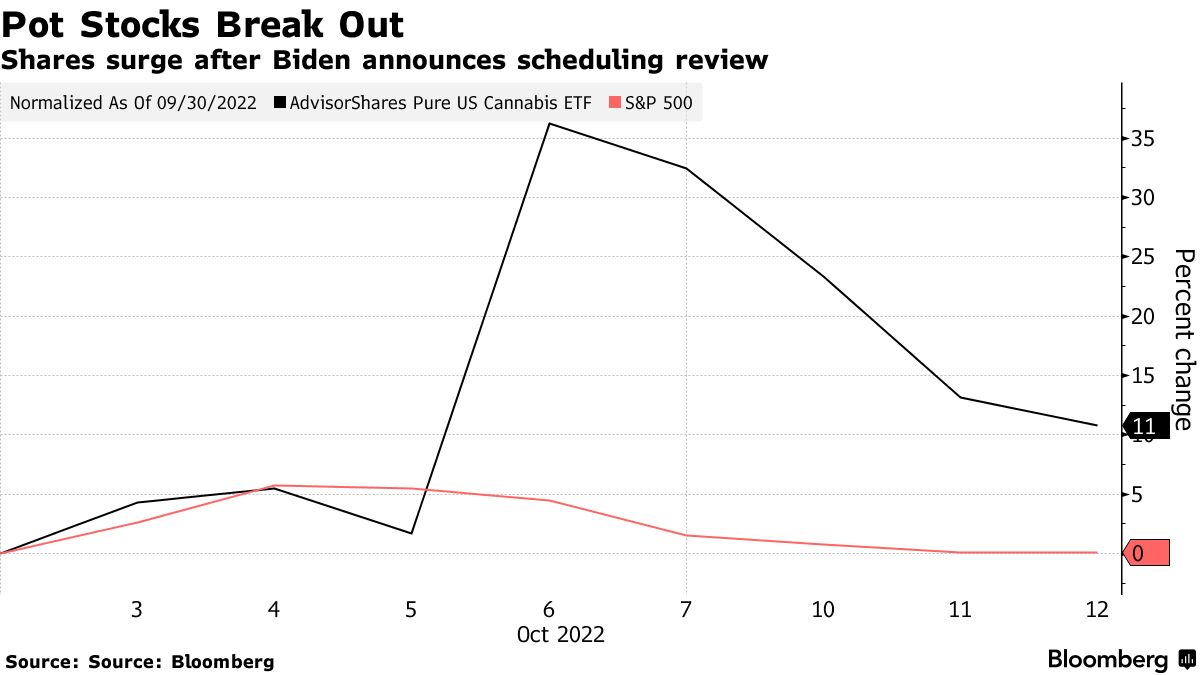
The biggest elephant in the room is the legal status of cannabis. While many countries and US states have legalized medical or recreational cannabis, it remains illegal at the federal level in the United States. This creates a complex and fragmented regulatory landscape. Because of this federal prohibition, most US-based cannabis companies can’t list their shares on major US stock exchanges like the NYSE or NASDAQ. Instead, they often trade on over-the-counter (OTC) markets, which are less regulated and generally have lower trading volumes.
This lack of federal clarity also makes it difficult for traditional financial institutions, like big banks, to provide funding to cannabis businesses. This pushes many smaller cannabis companies to raise capital through private investors or by issuing shares on these less prominent markets, where liquidity is naturally lower.
New and Developing Businesses
Many cannabis companies, especially the smaller ones, are still in their early stages of development. They might be focused on building their cultivation facilities, establishing distribution networks, or developing new products. This means they might not have the established track record, significant revenue, or widespread investor interest that larger, more mature companies enjoy. Without that broad interest, trading volume naturally stays low.
Limited Institutional Investment
Due to the regulatory uncertainties and the relatively nascent nature of the industry, many large institutional investors (think pension funds, mutual funds, and hedge funds) are hesitant or even legally restricted from investing in cannabis companies, especially those that “touch the plant” (meaning they are directly involved in cultivation, processing, or dispensing). This significantly reduces the pool of potential large-scale buyers and sellers, contributing to thin trading.
Niche Focus and Market Size
Some cannabis companies might focus on very specific niches within the industry, perhaps medical cannabis research, specific cannabinoid development, or niche recreational products. While these can be promising areas, they might appeal to a smaller segment of investors, leading to lower overall trading activity compared to a company targeting a broader market.
The Risks You Need to Know
Investing in any stock carries risk, but thinly traded cannabis stocks come with an amplified set of challenges. It’s crucial to understand these before you even think about putting your money in.
Price Volatility is Your Constant Companion
Because there are fewer buyers and sellers, even a relatively small trade can have a disproportionately large impact on the stock price. Imagine a tug-of-war with only a few people on each side – one person pulling harder can easily shift the whole rope. This means thinly traded cannabis stocks can experience wild price swings, jumping up or plummeting down quickly without much warning. This volatility can be exciting if you’re on the right side of a move, but it can also lead to significant and rapid losses.
Liquidity Risk: Getting Your Money Out
This is perhaps the biggest practical risk. If you own a thinly traded stock and decide you want to sell, you might struggle to find a buyer at a reasonable price, or at any price at all. You could be forced to sell at a much lower price than you’d like, or your order might sit there for days without being filled. This is known as “liquidity risk” – the risk that you can’t easily convert your investment into cash without affecting its market price. In extreme cases, you might not be able to sell at all, leaving you “stuck” with your shares.
Information Scarcity and Transparency Issues
Companies that are thinly traded, especially those on OTC markets, often have fewer reporting requirements than those listed on major exchanges. This can mean less publicly available information about their financials, operations, and future plans. It can be like trying to navigate a dense fog – you just don’t have all the details you need to make fully informed decisions. This lack of transparency can make it difficult to properly evaluate a company’s true value and prospects, increasing the risk of investing in something that might not be as robust as it appears.
Manipulation Concerns
With low trading volumes and less oversight, thinly traded stocks can be more susceptible to manipulation. A small group of individuals or even a single large investor could potentially influence the price by buying or selling significant blocks of shares, creating artificial demand or supply. This is sometimes seen in “pump-and-dump” schemes, where promoters artificially inflate a stock’s price and then sell their shares, leaving other investors with losses.
Regulatory Roadblocks Remain
Despite the progress in legalization, the overarching federal illegality in the US continues to cast a long shadow. Sudden shifts in political sentiment, unexpected crackdowns, or even simply a delay in anticipated federal reforms can significantly impact the entire cannabis sector, and thinly traded stocks, being more fragile, can feel these impacts even more acutely.
The Potential Upside: Why Some Take the Plunge
Given all the risks, you might wonder why anyone would even consider investing in thinly traded cannabis stocks. Well, like any high-risk, high-reward scenario, there’s a flip side with potentially significant benefits if things go right.
Early Entry into Growth Stories
Sometimes, thinly traded stocks represent smaller companies that are just starting to gain traction in a rapidly expanding market. If a particular cannabis company has a unique product, a strong management team, or secures a key license in a burgeoning market, getting in early before it becomes widely recognized could lead to substantial returns. These companies might be the future “blue chips” of the cannabis industry, and investing when they’re small and less liquid offers a chance to capitalize on that growth from the ground floor.
Undervalued Gems
Because they often fly under the radar of larger institutional investors and analysts, thinly traded cannabis stocks might occasionally be undervalued by the broader market. This means their current stock price might not fully reflect their true potential or assets. Astute individual investors who do their homework and identify these overlooked opportunities could see significant appreciation if the company gains more recognition or the market matures.
Catalyst-Driven Potential
The cannabis industry is constantly evolving with new regulations, scientific discoveries, and market developments. A thinly traded cannabis company could be sitting on a major catalyst – perhaps a successful clinical trial for a medical cannabis product, the legalization of cannabis in a new state or country where they have operations, or a strategic partnership with a larger entity. Such events can trigger a sudden surge in investor interest and, consequently, in the stock price.
Diversification (with Caution)
For some investors, thinly traded cannabis stocks might represent a way to diversify a portion of their portfolio into a high-growth, emerging sector. While this strategy carries considerable risk, a small allocation to these potentially explosive stocks could, in theory, boost overall portfolio returns if a few of them hit it big. However, it’s critical to emphasize that this should only be a small, speculative part of a well-diversified portfolio.
How to Approach Thinly Traded Cannabis Stocks for SEO Purposes (and Investment)
When crafting a long-form article about thinly traded cannabis stocks for SEO, the key is to provide immense value to the reader. This means going beyond surface-level information and truly educating them on the intricacies of this niche. For WordPress formatting, ensure you use headings effectively to break up the text and improve readability, even without images.
Thorough Research is Your Best Friend
Before writing about or investing in any thinly traded cannabis stock, you need to become an expert on it. This means:
Dig Deep into Financials
If available, pore over any financial statements. Look for revenue growth, profitability (or a clear path to it), debt levels, and cash flow. For thinly traded companies, this information might be harder to find, but any available data is crucial. Understand their business model inside and out – how do they make money? What are their costs?
Understand the Management Team
Who is running the show? What is their experience in the cannabis industry or in building successful businesses? A strong, experienced, and trustworthy management team is paramount for smaller, less established companies.
Scrutinize the Regulatory Landscape
Keep up-to-date on the legal and regulatory changes in the specific jurisdictions where the company operates. Federal, state, and even local laws can significantly impact a cannabis business.
Assess Competitive Advantage
What makes this particular company stand out? Do they have unique intellectual property, a strong brand, efficient cultivation methods, or a strategic market position? In a crowded and competitive industry, a clear competitive advantage is vital.
Focus on Value and Education
For SEO, your article should be a definitive resource. Answer every possible question a reader might have about thinly traded cannabis stocks. Use clear, concise language, and avoid jargon where possible. If you must use industry-specific terms, explain them clearly.
Structure for Readability and SEO
Long-form content thrives on good structure. Utilize H2 and H3 headings frequently to break up your content into digestible sections. This not only helps search engines understand your content’s hierarchy but also makes it much easier for readers to scan and find the information they’re looking for. Use bullet points and numbered lists to present complex information clearly.
Keyword Integration (Natural and Thoughtful)
While aiming for 2000+ words, naturally integrate relevant keywords and phrases throughout your article. Don’t “stuff” keywords; focus on providing valuable information. Think about what people would search for, such as “risks of cannabis penny stocks,” “investing in small cannabis companies,” or “volatile cannabis shares.”
Internal and External Linking
Link to other relevant articles on your website (internal links) to keep readers engaged and improve your site’s overall SEO. Also, include links to reputable external sources (like government reports, financial news sites, or academic studies) to back up your claims and enhance your article’s authority and trustworthiness.
Write for Humans, Optimize for Search Engines
Ultimately, Google wants to rank helpful, reliable, and user-friendly content. While SEO techniques are important, your primary focus should be on writing a compelling and informative article that genuinely helps your readers understand thinly traded cannabis stocks. If you do that, the SEO benefits will naturally follow.
Conclusion
Thinly traded cannabis stocks represent a fascinating, albeit risky, corner of the investment world. While the cannabis industry as a whole is experiencing significant growth and evolution, investing in these less liquid companies comes with heightened volatility, liquidity challenges, and often a lack of transparent information. The potential for outsized returns exists, driven by early-mover advantages, undervalued assets, or game-changing catalysts. However, these opportunities are shadowed by substantial risks, including price manipulation and the ever-present regulatory uncertainty. For anyone considering dipping their toes into this volatile market, thorough due diligence, a deep understanding of the inherent risks, and a clear investment strategy are not just recommended, but absolutely essential. Remember, only invest what you can afford to lose, and never confuse hope with a sound investment plan.
5 Unique FAQs After The Conclusion
FAQ 1: How can I identify if a cannabis stock is thinly traded?
You can identify a thinly traded cannabis stock by observing its daily trading volume, which will typically be quite low (e.g., a few thousand shares or less). Another strong indicator is a wide “bid-ask spread,” meaning a significant difference between the highest price buyers are willing to pay and the lowest price sellers are willing to accept. Major stock exchanges usually show this information directly on a stock’s quote page.
FAQ 2: Are thinly traded cannabis stocks more susceptible to “pump and dump” schemes?
Yes, thinly traded cannabis stocks, like other low-volume securities, are generally more susceptible to “pump and dump” schemes. This is because it takes relatively less capital and fewer transactions to significantly influence their price, making them attractive targets for manipulators who aim to artificially inflate the stock price before selling off their holdings, leaving other investors with losses.
FAQ 3: Can I invest in thinly traded cannabis stocks through a regular brokerage account?
It depends on the specific brokerage account and the exchange where the stock is traded. Many thinly traded cannabis stocks are listed on over-the-counter (OTC) markets, which some standard brokerage accounts may offer access to. However, some brokerages might have restrictions or require specific permissions for trading OTC securities due to their higher risk profile. Always check with your brokerage firm regarding their policies on trading OTC and thinly traded stocks.
FAQ 4: What kind of research should I prioritize before investing in a thinly traded cannabis stock?
Beyond basic financial analysis, prioritize understanding the company’s regulatory compliance, the experience and reputation of its management team, and any unique competitive advantages it possesses (e.g., proprietary technology, exclusive licenses, or a strong brand in a specific niche). Due to limited public information, seeking out news from industry-specific sources and analyzing any available investor presentations becomes even more critical.
FAQ 5: Is there a specific market capitalization range that typically defines a thinly traded cannabis stock?
While there’s no strict definition, thinly traded cannabis stocks often fall into the micro-cap or nano-cap range, meaning their market capitalization is relatively small, typically under $50 million, and sometimes even below $5 million. Companies in these market cap ranges often have lower public float (number of shares available for trading) and attract less institutional investor interest, leading to lower trading volumes.


